
The A to Z of THCa: What It Is, What It Does, and Where It Stands Legally
Why Understanding THCa Matters for Cannabis Users
What is THCa is a question more cannabis users are asking as this non-psychoactive cannabinoid gains attention. THCa, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is the raw, acidic form of THC in fresh cannabis plants that doesn't produce a "high" until heated.
Key Facts About THCa:
- Non-psychoactive in its raw form - won't get you high
- Precursor to THC - converts to psychoactive THC when heated
- Naturally occurring - found in fresh, unprocessed cannabis plants
- Potential benefits - early research suggests anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties
- Legal gray area - federally legal as hemp if under 0.3% Delta-9 THC
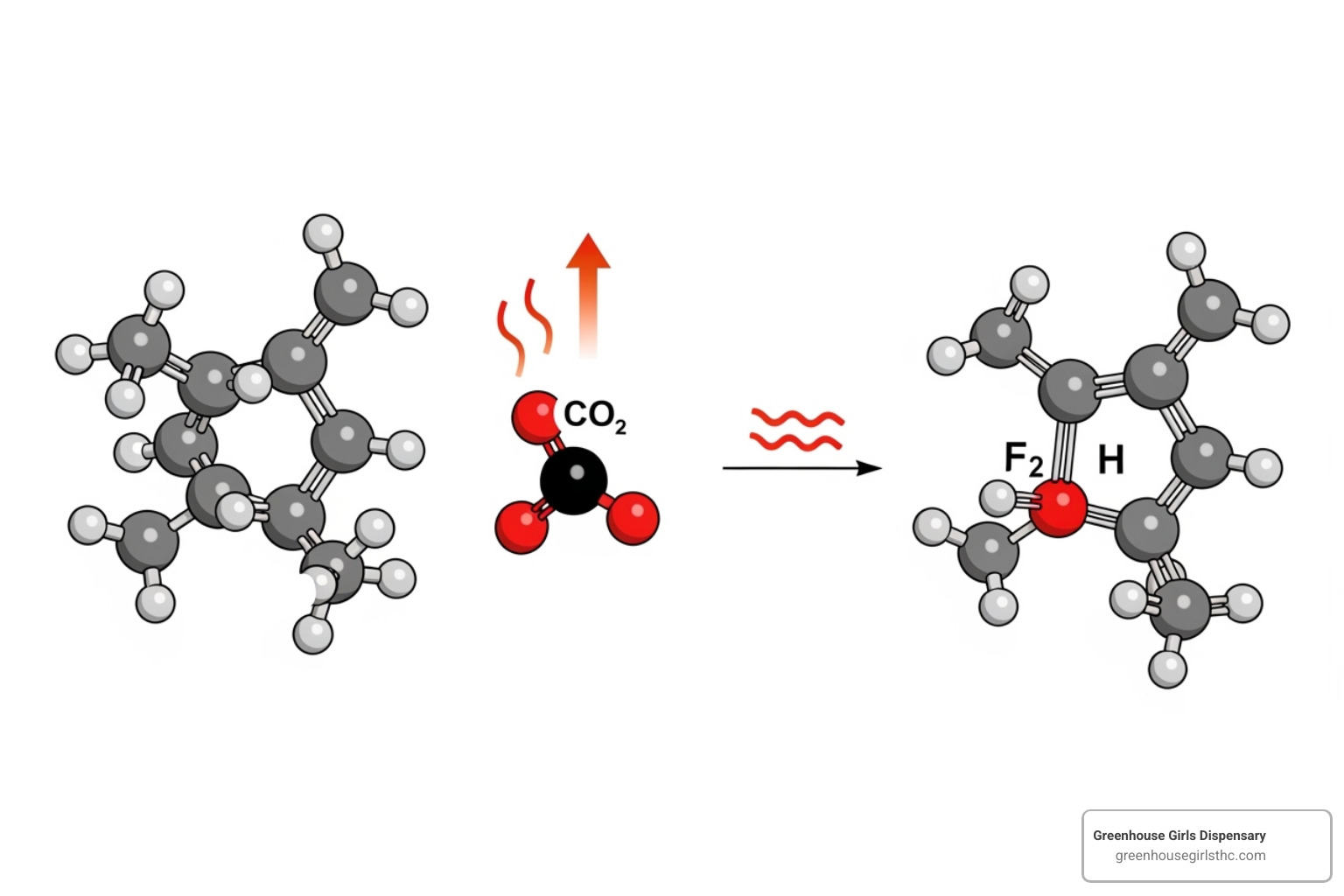
The confusion around THCa stems from its unique legal status and its change into THC through a simple process called decarboxylation. When you smoke, vape, or cook cannabis, heat removes a carboxylic acid group from the THCa molecule, converting it into the THC that produces psychoactive effects.
This distinction matters because THCa products offer a way to access potential cannabis benefits without intoxication—at least until you apply heat. Many users consume raw THCa through juicing, tinctures, or specially prepared products.
Through my work in cannabis education with Greenhouse Girls Dispensary and the National Cannabis Industry Association's Hemp Committee, I've seen how understanding these distinctions empowers consumers to make informed choices about their cannabis journey.
Unpacking the Science: What is THCa and How Does it Differ from THC?
The world of cannabis chemistry is fascinating. Fresh cannabis plants don't produce THC directly; instead, they are packed with THCa, a non-psychoactive precursor with incredible potential. Understanding what is THCa reveals that cannabis offers more than just a high, opening up possibilities for those seeking benefits without psychoactive effects. Let's explore the science.
What is THCa in the Cannabis Plant?
While THC gets attention for its psychoactive properties, THCa is the original cannabinoid acid in every living cannabis plant. In fresh, unprocessed cannabis, the plant's tiny, crystal-like trichomes produce THCa through biosynthesis. An enzyme called THCa-synthase transforms cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) into THCa, the plant's most important cannabinoid.
Scientists believe THCa plays a crucial role in plant defense, protecting the plant from natural threats. However, THCa is unstable. Scientific research on THCa's instability shows that even at cool temperatures (39-64°F), THCa slowly converts to THC. This means freshly harvested plants won't stay non-psychoactive forever.
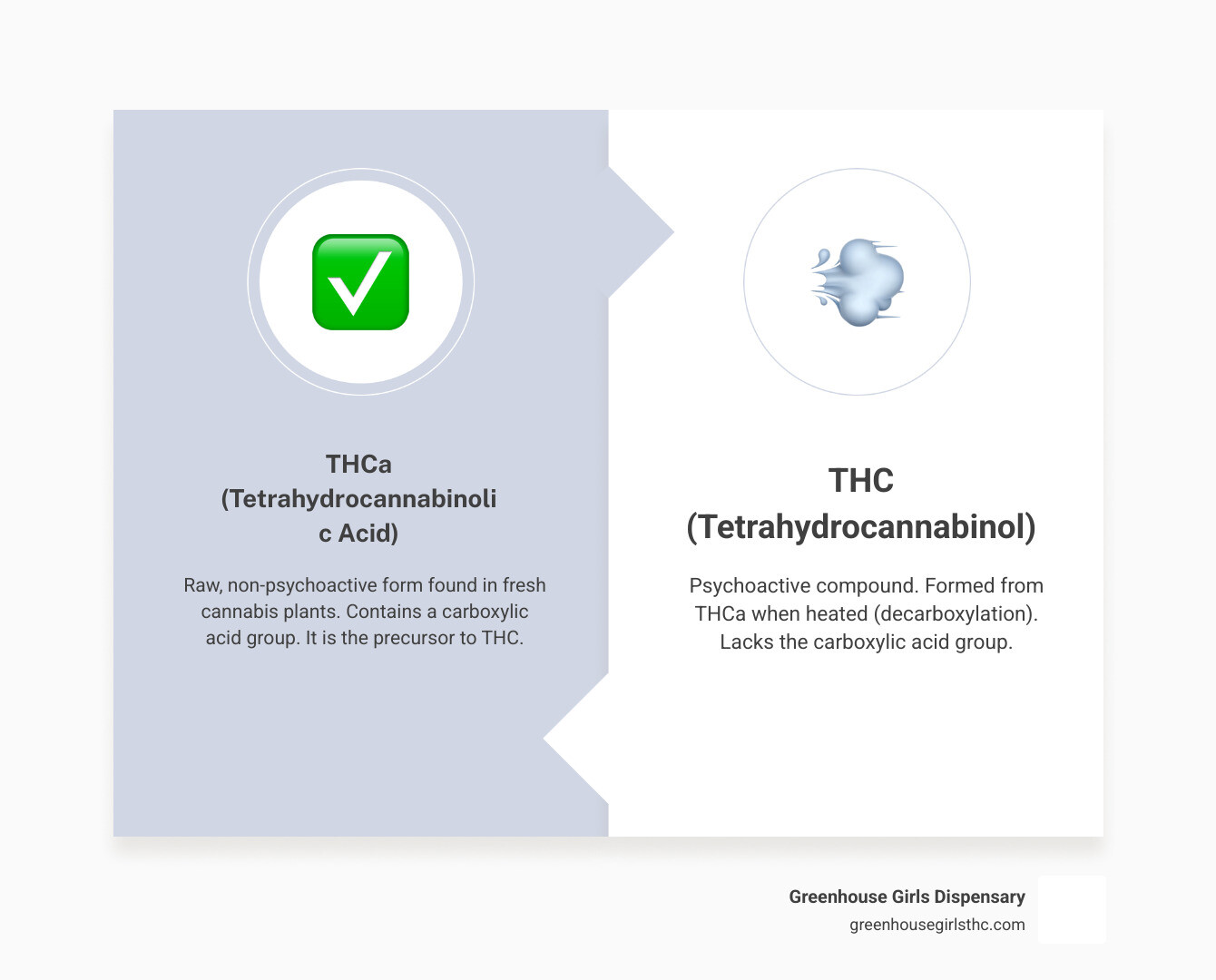
The Key Difference: THCa vs. THC
The difference between THCa and THC is a single carboxylic acid group. This small molecular addition changes how the compounds behave in your body.
THCa has this extra group, making its molecule too large to fit into the brain's CB1 receptors. Since it can't bind to these receptors, THCa won't get you high.
THC, however, has lost that acid group. This allows it to fit perfectly into CB1 receptors, creating the euphoric, psychoactive effects cannabis is known for.
| Feature | THCa (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) | THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) |
|---|---|---|
| Psychoactivity | Non-psychoactive | Psychoactive |
| Chemical Form | Acidic form (contains COOH group) | Neutral form (lacks COOH group) |
| Presence in Plant | Abundant in raw, fresh cannabis | Formed from THCa via decarboxylation |
| Receptor Binding | Low affinity for CB1/CB2 receptors | High affinity for CB1 receptors |
| Common Consumption | Raw (juicing, tinctures, edibles without heat) | Heated (smoking, vaping, edibles) |
| Legal Status | Often considered hemp (if <0.3% D9-THC), legal gray area | Federally controlled (Schedule I) in most forms, state-legal in some areas |
The legal status overview gets particularly interesting here. While THC remains federally controlled, THCa often falls into a legal gray area, especially when derived from hemp. This distinction has opened doors for people in states where traditional THC products aren't available.
If you're curious about how different cannabinoids stack up against each other, our guide on THC vs. CBD: What's the Difference? Which One's Right For You? dives deeper into these important comparisons.
How THCa Becomes THC: The Decarboxylation Process
Decarboxylation is the simple process where heat removes the carboxylic acid group from THCa, changing it into THC.
- Smoking causes instant decarboxylation, converting nearly 95% of THCa into THC upon lighting.
- Vaping provides more control, decarboxylating THCa at specific temperatures (315-440°F) without combustion for a smoother experience.
- Cooking edibles requires a preliminary decarboxylation step, typically baking cannabis at around 230°F for 30-90 minutes. This is crucial, as eating raw cannabis is not psychoactive. The conversion rate is usually 70-90%.
Even light exposure and room temperature storage will slowly convert THCa to THC, which is why proper storage is vital for preserving THCa's non-psychoactive properties. Understanding this process explains why the same plant can offer different experiences: raw THCa for potential therapeutic benefits without intoxication, and heated THC for the classic cannabis effects.
The Potential of Raw THCa: Exploring Benefits, Effects, and Side Effects
While the psychoactive effects of THC have long dominated the cannabis conversation, the non-intoxicating nature of raw THCa is opening up new avenues for wellness. Because THCa doesn't bind to the CB1 receptors that cause a "high," we can explore its potential therapeutic benefits without intoxication. This interaction with the body's endocannabinoid system (ECS) and other pathways is what makes THCa so intriguing.
Potential Health Benefits of THCa
Preliminary research, mostly in early stages and on animals, suggests THCa may offer several health benefits for those seeking therapeutic properties without psychoactive effects.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: THCa shows significant promise as an anti-inflammatory agent, which could benefit conditions like arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Studies suggest THCa may help support brain health and guard against neurodegenerative diseases. Early research on neuroprotective properties indicates THCa acts as a potent PPARγ agonist, contributing to this activity.
- Anti-emetic Properties: THCa has been shown to reduce nausea and vomiting, with one study suggesting it may be more effective than THC for these symptoms.
- Appetite Stimulation: Like THC, THCa may also help stimulate appetite for those struggling with appetite loss.
- Epilepsy Treatment: A 2017 study indicated THCa might be an effective treatment for epilepsy at small doses, though higher doses seemed to worsen symptoms, highlighting the need for precise dosing.
- Antioxidant Activity: THCa may possess antioxidant properties, helping protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
This research is preliminary and requires more human studies, but the initial findings are promising.

How THCa Interacts with the Body
THCa interacts with our bodies differently than THC. Its larger molecular structure prevents it from binding effectively with the CB1 and CB2 receptors of our endocannabinoid system (ECS), which is why it isn't intoxicating.
However, a lack of direct binding doesn't mean THCa has no effect. Current THCA research on receptor binding suggests that THCa interacts with various other enzymes and receptors. For instance, it acts as a potent PPARγ agonist, linked to its neuroprotective activity. It also interacts with enzymes like COX-1 and COX-2 (involved in inflammation) and various transient receptor potential (TRP) channels. This complex interaction with multiple pathways contributes to its diverse potential therapeutic effects.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While raw THCa is non-psychoactive, potential risks relate to its conversion to THC, product quality, and individual sensitivities.
- Conversion to Psychoactive THC: The primary risk is THCa's easy conversion to THC with heat. Smoking or vaping a high-THCa hemp flower is equivalent to consuming high-THC cannabis. The CDC notes these products can reach 15-20% total THC when heated, turning federally compliant hemp into potent marijuana upon consumption.
- Unregulated Products and Contamination Risk: The evolving market for hemp-derived products can lack stringent quality control. Untested products might contain contaminants like pesticides or heavy metals. Always buy from reputable suppliers who provide lab testing.
- Drug Test Implications: Consuming THCa, even raw, can lead to a positive drug test. Your body can metabolize THCa into THC-COOH, the compound screened for in drug tests. Avoid all cannabis products, including THCa, if you are subject to testing.
- Individual Sensitivity and Tolerance: Responses to THC vary. Some people experience anxiety or paranoia, especially with high doses. If you are new to cannabis, start with a very low dose to assess your tolerance.
- Psychological Addiction: While raw THCa is not addictive, the THC it converts into can be psychologically addictive, leading to dependence with habitual use.
- Respiratory Issues from Heating: Smoking or vaping THCa products carries the same potential long-term respiratory risks as traditional cannabis consumption.
We advise customers to exercise caution and make informed decisions.
Navigating the World of THCa: Legality, Forms, and Safe Consumption
Navigating THCa can feel complex, but with the right knowledge, you can confidently explore this cannabinoid and make informed choices about what you're putting in your body.
Is THCa Legal? The Complex Regulatory Landscape
The legal status of what is THCa is complex, stemming from the 2018 Farm Bill.
The 2018 Farm Bill federally legalized hemp, defining it as cannabis with 0.3% Delta-9 THC or less by dry weight. Marijuana, with higher concentrations, remains federally controlled. The confusion arises because this limit often refers to total THC (Delta-9 THC plus potential THC from THCa conversion).
A "loophole" exists because THCa itself is non-psychoactive. Products high in THCa but low in Delta-9 THC can be sold as hemp. However, when heated, this THCa flower can become 15% to 20% potent in THC, like traditional marijuana.
This creates a legal gray area. THCa could fall under the Federal Analogue Act, which treats substances chemically similar to controlled substances as if they were scheduled. Its easy conversion to THC puts it at risk of prosecution under this act.
State-specific laws add more complexity. Where cannabis is legal, THCa is generally accepted. In other states, it exists in murky legal waters. Always check your local laws.
For our Florida customers, our guide on Delta 9 gummies legality can help clarify the local landscape.
What are the Different Forms of THCa?
The beauty of cannabis lies in its versatility, and THCa is no exception. At Greenhouse Girls Dispensary, we're proud to offer federally legal, lab-tested, hemp-derived cannabis products sourced from small family farms across the country. Our commitment to quality means every product comes with transparency and peace of mind.
- THCa flower is essentially raw, uncured hemp cannabis cultivated to have high levels of THCa while staying under the 0.3% Delta-9 THC limit. When smoked or vaped, heat converts the THCa to THC. We've written a guide about what THCa flower is if you want to dive deeper.
- Crystalline and diamonds are nearly pure THCa isolate. When dabbed at high temperatures, they convert instantly to THC, delivering a potent experience not for beginners.
- Tinctures and topicals offer therapeutic benefits without psychoactive effects. THCa tinctures can be taken sublingually or mixed into cold foods, while topicals provide localized relief without entering the bloodstream in significant amounts.
- Raw cannabis for juicing is the purest approach. Juicing fresh leaves and buds maximizes the intake of cannabinoids in their natural, acidic forms.
Safe Consumption Practices for THCa
Practicing safe consumption is essential with THCa. At Greenhouse Girls Dispensary, we believe knowledge empowers better choices.
- Start low and go slow: This is the golden rule, especially with products that convert THCa to THC like flower or diamonds. Begin with a tiny amount and wait to assess your body's response.
- Source from reputable suppliers: Choosing suppliers like Greenhouse Girls Dispensary ensures you receive federally legal, lab-tested products from trusted farms, avoiding the risks of unregulated items.
- Read lab reports (COAs): Certificates of Analysis are your best friend. Reputable suppliers provide third-party lab reports detailing the cannabinoid profile and confirming the product is free of contaminants. Always check the COA.
- Understand the conversion process: Heating THCa converts it to THC. To avoid psychoactive effects, stick to raw consumption methods like tinctures or topicals designed to preserve THCa.
- Proper storage: Store THCa products in a cool, dark place to prevent unintended conversion to THC and keep them away from children and pets.
- Seek medical advice: Consult your healthcare provider if you have underlying health conditions, are pregnant or breastfeeding, or take other medications.
By following these practices, you can confidently explore THCa's potential benefits while minimizing risks.
Frequently Asked Questions about Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid
Throughout my years in cannabis education and working with customers at Greenhouse Girls Dispensary, I've noticed that certain questions about THCa come up again and again. These are the ones that really matter to people who are trying to understand this fascinating cannabinoid.
Does consuming raw THCa get you high?
No, consuming raw THCa will not get you high. In its natural state, what is THCa is a non-psychoactive compound. Its molecular structure is too large to bind with the brain's CB1 receptors that cause a "high."
The key word here is raw. Consuming unheated THCa in juices, tinctures, or other raw products will not cause intoxication. It only becomes psychoactive THC when heated through smoking, vaping, or cooking. This is why raw THCa appeals to those seeking cannabis wellness without mind-altering effects.
Will THCa show up on a drug test?
Yes, THCa consumption can potentially lead to a positive drug test. Most drug tests screen for THC-COOH, a metabolite your body creates when processing THC. Your body can also metabolize THCa into this same compound.
Even with raw consumption, some THCa may convert to THC due to storage, processing, or even digestion. If you are subject to drug testing, we strongly recommend avoiding all cannabis products, including those high in THCa, to prevent a positive result.
Is THCa natural or synthetic?
THCa is completely natural. It develops organically in cannabis plants as they grow. Enzymes within the plant's trichomes convert other cannabinoids into THCa as part of its natural life cycle, requiring no human intervention or lab synthesis.
Unlike synthetic cannabinoids, THCa is as natural as the plant itself. This is why it can fit into the legal hemp category. Natural THCa also comes with a full spectrum of other plant compounds like terpenes and flavonoids that contribute to the "entourage effect."
Finding High-Quality THCa for Yourself
Understanding what is THCa empowers you as a cannabis consumer. It offers a compelling option for those seeking cannabis benefits without psychoactive effects, or for those looking for federally legal alternatives that convert to THC.

At Greenhouse Girls Dispensary, we are passionate about providing high-quality, transparent, and federally legal cannabis. Our THCa flower and other hemp-derived products are sourced from small family farms, ensuring superior quality. Every product is lab-tested, and you can always check the Certificate of Analysis to know exactly what you're getting.
Whether you're in Palm Harbor, Oldsmar, Florida, or anywhere nationwide, we deliver to your door. We're proud to offer legal access to high-quality cannabis alternatives and are currently offering a free Baby Jay with your order!
We encourage you to explore the difference between hemp-derived and marijuana-derived cannabis and find the potential of THCa for yourself. Your informed cannabis journey starts here.






